Before and After Taxes and Transfers - Singapore’s Gini Coefficient
19 Mar 20181. There are different methodologies used internationally for calculating the Gini coefficient. Singapore’s Gini coefficient is typically reported based on household income from work per household member. The calculation
by the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) is based on the Square Root Scale[1].
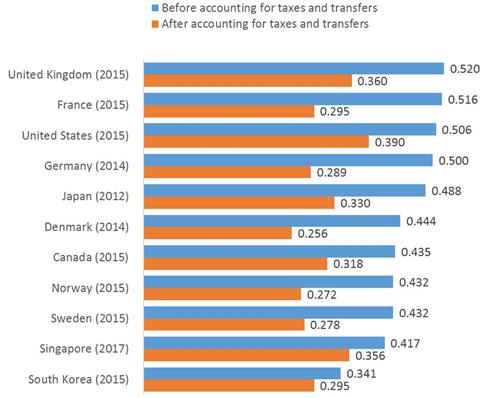
2. If we apply the OECD method to ourselves, then based on data from
the latest available year, the Gini coefficients for Singapore and some major economies are shown in Chart 1.
3. Before taxes and transfers, Singapore’s Gini coefficient is low compared with many major developed
economies.
4. After taxes and transfers, several countries have a lower Gini coefficient compared to Singapore. This is because they typically impose higher overall taxes on the working population and in particular on
the middle-income, in order to finance large social transfers. In contrast, Singapore’s approach is to keep our tax burden low, and provide targeted support for the lower-income.
5. In addition, these calculations
do not reflect the full range of Government policy interventions that are unique to the Singapore context. For example, many Singaporeans enjoy significant subsidies for the purchase of HDB flats, which have helped them own homes in a high-quality
living environment.
Chart 1: International comparison of Gini coefficients based on the square root scale (latest available year)[2]
---
[1] Equivalence scales are used to
adjust for household size so that the incomes of households of different sizes and compositions are comparable to each another. Details can be found in the Department of Statistics’ Key Household Income Trends publication, downloadable from
https://www.singstat.gov.sg/publications/publications-and-papers/population#household_income.
[2] Singapore’s Gini is based on household income from work whereas data on OECD economies is based on income from all sources (which includes non-work income from investments and property). For further details, please refer to MOF’s
Occasional Paper on Income Growth, Distribution and Mobility Trends in Singapore which can be downloaded from https://www.mof.gov.sg/Resources/Feature-Articles/Income-Growth-Distribution-and-Mobility-Trends-in-Singapore.
